binary digit calculation and game
 |
| binary digit calculation and game |
The bit (read bits, denoted as b) is the basic unit of information in Computer Science and Telecommunications. One bit is the amount of information that can be stored by a binary device or other physical system which can exist in one of two distinct states (for example, these situations can be the two positions of a switch, the two voltages Electricity allowed in a circuit, etc.).
In computer science, a bit may further be defined as a variable, or an appreciable amount which can have only two possible values. These two values are usually interpreted as binary digits are represented by numbers 0 and 1. bit word in English is clear from the words Binary DIGIT , but literally mean "tiny portion, piece '. In Greek assigned bit (in the CD, and following the reasoning of the English abbreviation), the abbreviation of bits , a term not used at all in the literature. The two values that can take a bit can be interpreted as logical values (true / false, yes / no), as variables (true / false, yes / no), as algervika signs (+ /;), as on state ( on / off, on / off), or any other attribute which can take only two values.
The computers work with the binary numbering system and use bits to represent commands and data. In physical terms, the values 0 and 1 are implemented in hardware as statements electrical conductivity of a transistor, that is power or not is power. Computers typically use the bit in groups of 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 etc., i.e. powers of 2.
The byte (byte) (denoted by B) is a unit of quantity of information in computer systems. A byte equals 8 bit, i.e.
Vyte 1 = 8 bits .
To byte can represent values from 0 to 255 in decimal system (28 = 256 values). Generally a series of  bits representing
bits representing 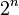 different values.
different values.
 bits representing
bits representing 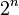 different values.
different values.
Multiples of byte are:
- Kilobytes (kilobytes), 1 kB = 1,024 bytes = the 2nd the 10th bytes
- Megabytes (megabytes), 1 MB = 1,048,576 bytes on the 2nd = 20 bytes
- GIGABYTE (gigabytes), 1 GB = 1,073,741,824 bytes = two the 30th bytes
- Terabyte (Terabyte), 1 TB = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes = the 2nd 40 bytes
- Petabyte (Petabyte), 1 PB = 1125899906842624 = 2 bytes 50 bytes
- Exabyte (Exabyte), one EB = 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 two bytes = 60 bytes
- Zettabyte (Zettabyte), 1 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 ZB = 2 bytes = 70 bytes
- Yottabyte (Giotampait), on the 1st YB = 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 the 2nd bytes = 80 bytes
EXAMPLE
To better understand the bits and bytes will see the following example. Suppose we have 8 switches in a row and each switch corresponds to the numbers as shown in the picture.
These switches represent 1 byte information consisting of 8 bits. Notice that each number is obtained by a power of 2. So:
2 ^ 0 = 1
2 1 = 2 ^
2 ^ 2 = 4
2 ^ 3 = 8
2 ^ 4 = 16
2 ^ 5 = 32
2 ^ 6 = 64
2 ^ 7 = 128
2 ^ 0 = 1
2 1 = 2 ^
2 ^ 2 = 4
2 ^ 3 = 8
2 ^ 4 = 16
2 ^ 5 = 32
2 ^ 6 = 64
2 ^ 7 = 128
When all switches are closed, formed the number 0. When you open the last switch, formed the number 1. When you open the penultimate switch, formed the number 2, and so If it is open the latter two switches formed by the number 3 (2 + 1 = 3), if it is open the last three, the number 7 is formed so When it is open all switches formed the number 255.
Open and close the switches to form different numbers! You can find the number 92? The number 31? The number 64?
binary game
Like the Post? Share with your Friends:-










0 comments:
POST A COMMENT